Ovulation Regulation — Simple ways to track, control, or boost your cycle
Want clearer control over your cycle? Whether you’re avoiding pregnancy, trying to conceive, or fixing irregular cycles, knowing how ovulation works gives you power. Ovulation is when an ovary releases an egg — usually once per cycle — and changing hormones, weight, stress or health conditions can shift timing or stop it entirely.
Practical ways to track ovulation
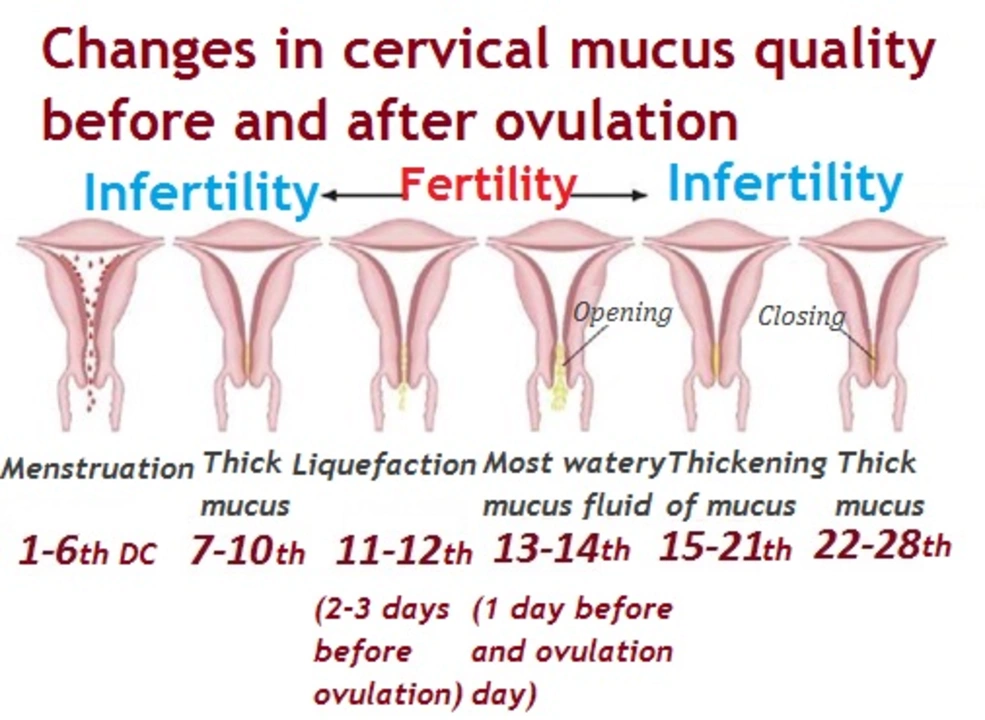
Start with the basics: calendar, signs, and quick tests. Track cycle length for three months to see your pattern. Use an ovulation predictor kit (OPK) to detect the LH surge 24–48 hours before ovulation — very handy if your cycles are regular. Check cervical mucus: thin, stretchy and clear mucus usually means ovulation is near. Take your basal body temperature (BBT) every morning; a small, sustained rise means ovulation already happened. Apps can help log this data, but don’t rely on them alone.
Timing tip: sperm live up to five days, the egg about 24 hours. If you’re trying to conceive, aim for sex in the 3–4 days before and the day of ovulation. If avoiding pregnancy, combine tracking with another reliable method — tracking alone can miss surprises.
Ways to control or induce ovulation
Hormonal birth control prevents ovulation. Combined pills, patches, rings, injections, implants and certain IUDs stop the egg from releasing — pick the method that fits your lifestyle and health. If you want to start/stop these methods, talk to your provider about timing to avoid gaps in protection or unwanted bleeding changes.
If you’re not ovulating and want to conceive, doctors may prescribe medications. Clomiphene (Clomid) and letrozole (Femara) are common first steps; they stimulate the brain to prompt the ovaries to release eggs. Injectable gonadotropins are stronger but need clinic monitoring because they raise the risk of multiple pregnancies and ovarian hyperstimulation. Your doctor will often check blood hormones (AMH, FSH) and do an ultrasound before recommending treatment.
Lifestyle matters. Aim for a stable, healthy weight — both low and high BMI can stop ovulation. Cut heavy smoking, limit alcohol, and don’t overdo intense exercise. Small changes like balanced meals, moderate activity, good sleep and stress reduction often improve cycle regularity.
When to see help: if cycles are very irregular, absent for several months, you have severe acne, excess hair, or trouble conceiving after six months (if over 35, try for three months first). Fertility specialists can run tests, treat underlying issues like PCOS or thyroid problems, and map a clear plan.
Bottom line: you can track and influence ovulation with simple tools, medicines, or lifestyle shifts. Talk with your clinician to pick safe options that match your goals — pregnancy planning, reliable contraception, or fixing irregular cycles all need slightly different approaches.
The effects of thyroid disorders on the regulation of ovulation and menstruation
Apr 29, 2023, Posted by Mike Clayton
In my latest blog post, I discussed the significant impact thyroid disorders can have on the regulation of ovulation and menstruation. I found that both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can lead to irregular periods and even infertility. It's crucial to understand that thyroid hormones are directly involved in regulating reproductive hormones, which in turn affect the menstrual cycle. Early detection and appropriate treatment of thyroid disorders can help in restoring normal menstrual function and improving fertility. It's essential to consult with a healthcare professional if you suspect any issues with your thyroid, as addressing the problem can make a huge difference in your overall health and well-being.
MORESEARCH HERE
Categories
TAGS
- treatment
- online pharmacy
- dietary supplement
- side effects
- generic drugs
- medication adherence
- medication safety
- health
- dietary supplements
- health benefits
- online pharmacy Australia
- generic substitution
- adverse drug reactions
- thyroid disorders
- gabapentin
- treatment option
- calcipotriol
- blood pressure
- erectile dysfunction
- closer look
