Oral Medication Effectiveness: How Your Body Absorbs and Uses Pills
When you swallow a pill, oral medication effectiveness, how well a drug works after being taken by mouth. It’s not just about the dose—it’s about whether your body can actually use it. Many people assume if a pill is prescribed, it will work the same for everyone. But that’s not true. Factors like stomach acid, food, other drugs, and even your genetics change how much of the medicine actually enters your bloodstream. This is called bioavailability, the proportion of a drug that enters circulation and can have an active effect. A drug with low bioavailability might need a higher dose—or might not work at all if taken with the wrong meal.
Take drug interactions, when one medication changes how another behaves in the body. Cranberry juice can make warfarin too strong. Grapefruit can turn a statin into a dangerous overload. Even something as simple as taking metformin with contrast dye can trigger rare but serious side effects. These aren’t rare edge cases—they’re common mistakes that lead to hospital visits. And it’s not just about what you take with your pill. Timing matters. Taking antibiotics on a full stomach might stop them from working. Some blood pressure pills work better in the morning, others at night. Your body’s rhythm affects how drugs are absorbed.
medication adherence, how consistently a patient takes their medicine as prescribed. is the biggest hidden factor in oral medication effectiveness. If you skip doses, crush pills, or stop because of side effects, the drug can’t do its job—even if it’s perfectly designed. That’s why bringing your actual pill bottles to doctor visits isn’t just helpful—it’s critical. Doctors can’t fix what they can’t see. And when you’re on multiple drugs, the risk of confusion grows. One wrong pill, one missed dose, and your whole treatment can unravel.
Oral medication effectiveness isn’t magic. It’s science. It’s biology. It’s your habits meeting chemistry. Some pills are designed to dissolve slowly. Others need to bypass your stomach. Some work better with fat, others need an empty gut. The difference between a drug working and failing isn’t always the prescription—it’s how you take it. And that’s where most people get left behind.
Below, you’ll find real-world guides on what actually affects how your pills work—from how antibiotics cause confusion in older adults, to why some statins wreck your muscles, to how to tell if your antidepressant is doing anything at all. These aren’t theory pieces. They’re what patients and doctors actually deal with every day. If you’re on any oral medication, this is the stuff you need to know.
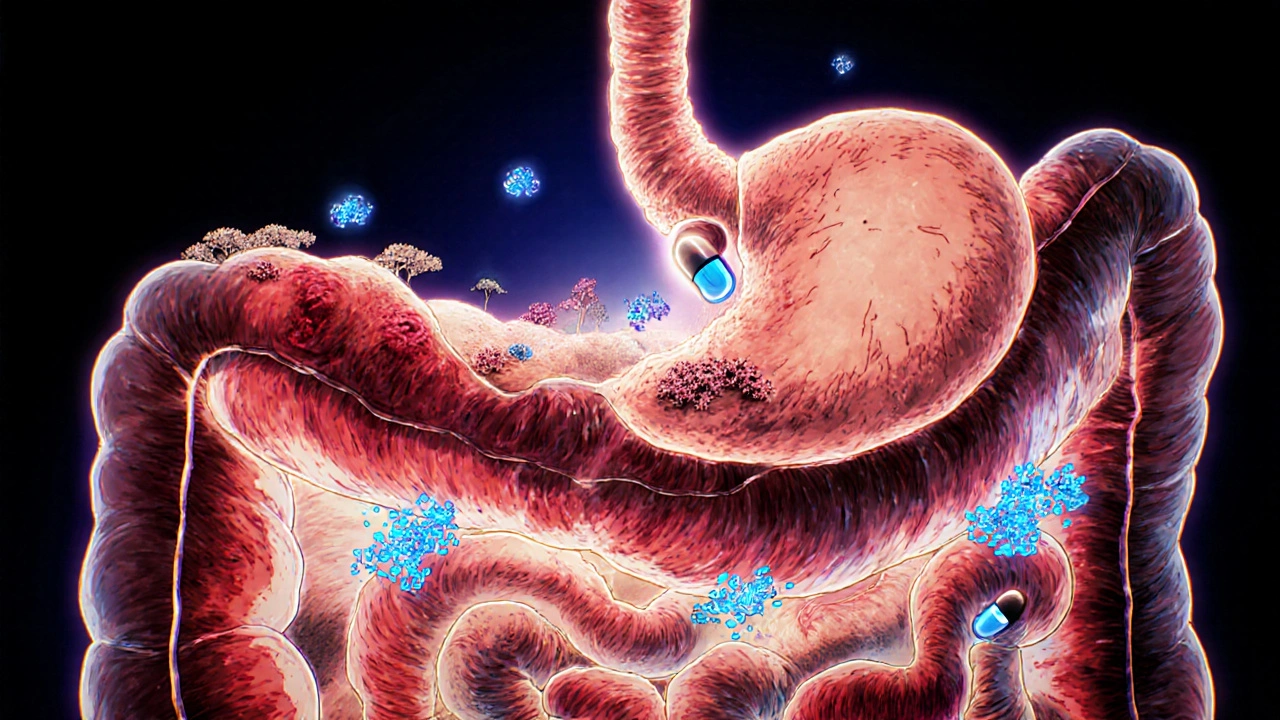
Gastrointestinal Medications: Why Absorption Problems Ruin Effectiveness
Nov 29, 2025, Posted by Mike Clayton
Many gastrointestinal medications fail to work because of poor absorption in the gut. Learn how food, disease, pH, and formulation affect drug effectiveness-and what you can do about it.
MORESEARCH HERE
Categories
TAGS
- treatment
- online pharmacy
- dietary supplement
- side effects
- generic drugs
- medication adherence
- medication safety
- health
- dietary supplements
- health benefits
- online pharmacy Australia
- generic substitution
- adverse drug reactions
- thyroid disorders
- gabapentin
- treatment option
- calcipotriol
- blood pressure
- erectile dysfunction
- closer look
