Drug Absorption: How Your Body Takes in Medication and Why It Matters
When you swallow a pill, drug absorption, the process by which a medication enters your bloodstream from where it’s taken. Also known as bioavailability, it determines whether that pill actually does anything in your body. A drug might be perfectly formulated, but if your body can’t absorb it properly, it’s just wasted money—and maybe even a missed opportunity to feel better. This isn’t just about whether the pill dissolves; it’s about how fast, how much, and where it gets into your system. That’s why two people taking the same dose can have totally different results.
Gastrointestinal absorption, how drugs move from your stomach and intestines into your blood, is the most common path. But it’s messy. Food can block it, acid levels can break it down too soon, and some drugs just refuse to cross the gut lining. Take drug interactions, when one substance changes how another is absorbed. Cranberry juice messing with warfarin? That’s absorption. Metformin and contrast dye affecting kidney clearance? That’s absorption. Even something as simple as taking your antibiotic with milk instead of water can cut its effectiveness in half.
It’s not just about what you take—it’s when and how. Some meds need an empty stomach. Others need food to even work. Your age, your gut health, your liver, your kidney function—all of it changes how drugs get in. Older adults absorb drugs slower. People with Crohn’s or celiac disease might absorb barely anything. And if you’re on multiple meds, the chances of one drug blocking another’s absorption go up fast. That’s why bringing your actual pill bottles to your doctor isn’t just a good idea—it’s a safety net.
What you’re about to read isn’t theory. It’s real stories from people who learned the hard way that absorption matters. You’ll find out why some statins cause more muscle pain because of how they’re absorbed, how antibiotics can trigger confusion in seniors due to brain penetration, and why your vitamin K intake can swing your INR levels without you even realizing it. These aren’t abstract concepts—they’re daily realities for millions. Whether you’re managing blood pressure, diabetes, depression, or just trying to avoid a bad reaction, understanding drug absorption is the first step to making your meds actually work for you.
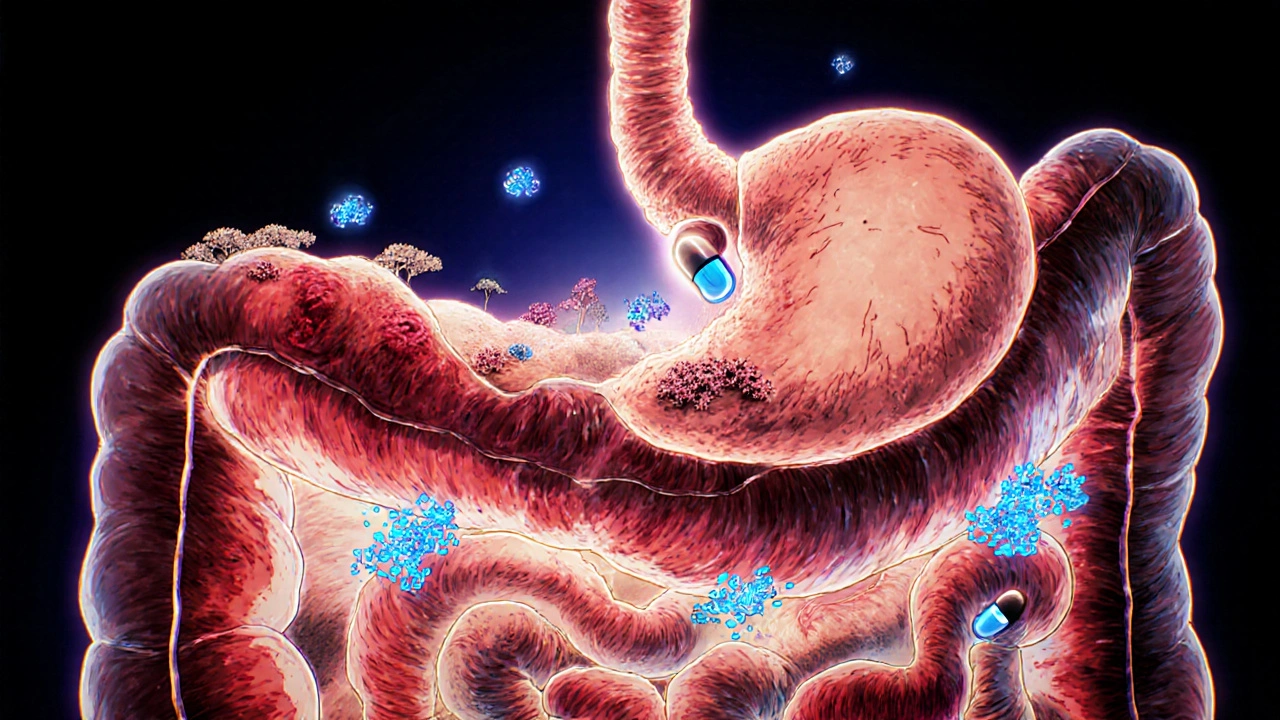
Gastrointestinal Medications: Why Absorption Problems Ruin Effectiveness
Nov 29, 2025, Posted by Mike Clayton
Many gastrointestinal medications fail to work because of poor absorption in the gut. Learn how food, disease, pH, and formulation affect drug effectiveness-and what you can do about it.
MORESEARCH HERE
Categories
TAGS
- treatment
- online pharmacy
- dietary supplement
- side effects
- generic drugs
- medication adherence
- medication safety
- health
- dietary supplements
- health benefits
- online pharmacy Australia
- generic substitution
- adverse drug reactions
- thyroid disorders
- gabapentin
- treatment option
- calcipotriol
- blood pressure
- erectile dysfunction
- closer look
