Medication Bioavailability: What It Means and Why It Affects Your Health
When you take a pill, it doesn’t automatically work the way you expect. Medication bioavailability, the percentage of a drug that enters your bloodstream and becomes available to have an effect. It’s the difference between what’s in the bottle and what actually reaches your cells. Two people taking the same dose of the same drug can have wildly different results—not because one is "stronger," but because of how their bodies handle absorption, metabolism, and delivery.
That’s where drug absorption, how quickly and completely a medicine moves from the gut into the blood comes in. A drug with low bioavailability might need a higher dose to work, or it might not work at all if taken with food, antacids, or other meds. For example, generic drugs, medications approved as equivalent to brand-name versions must meet strict bioavailability standards—but small differences in fillers or coating can still change how fast or how much gets into your system. That’s why some people notice a difference when switching brands, even when the active ingredient is identical.
It’s not just about pills, either. drug interactions, when one substance changes how another behaves in the body can slash bioavailability. Grapefruit juice, for instance, can block enzymes that break down certain blood pressure and cholesterol drugs, making them too strong. On the flip side, some antibiotics can speed up metabolism, leaving you with too little of the drug in your system. Even your gut health, liver function, or kidney disease can alter how your body handles medication.
Understanding medication bioavailability helps you ask the right questions. Why did your doctor switch your statin? Why does your antidepressant seem less effective after a stomach bug? Why does your blood thinner need regular tests? These aren’t random changes—they’re responses to how your body processes drugs. The posts below dive into real cases: how warfarin interacts with vitamin K, why metformin needs kidney checks, how statins cause muscle pain, and why bringing your actual pill bottles to appointments matters. You’ll see how bioavailability isn’t just science—it’s personal. It’s the hidden reason your meds work, or don’t. And knowing that can change how you manage your health.
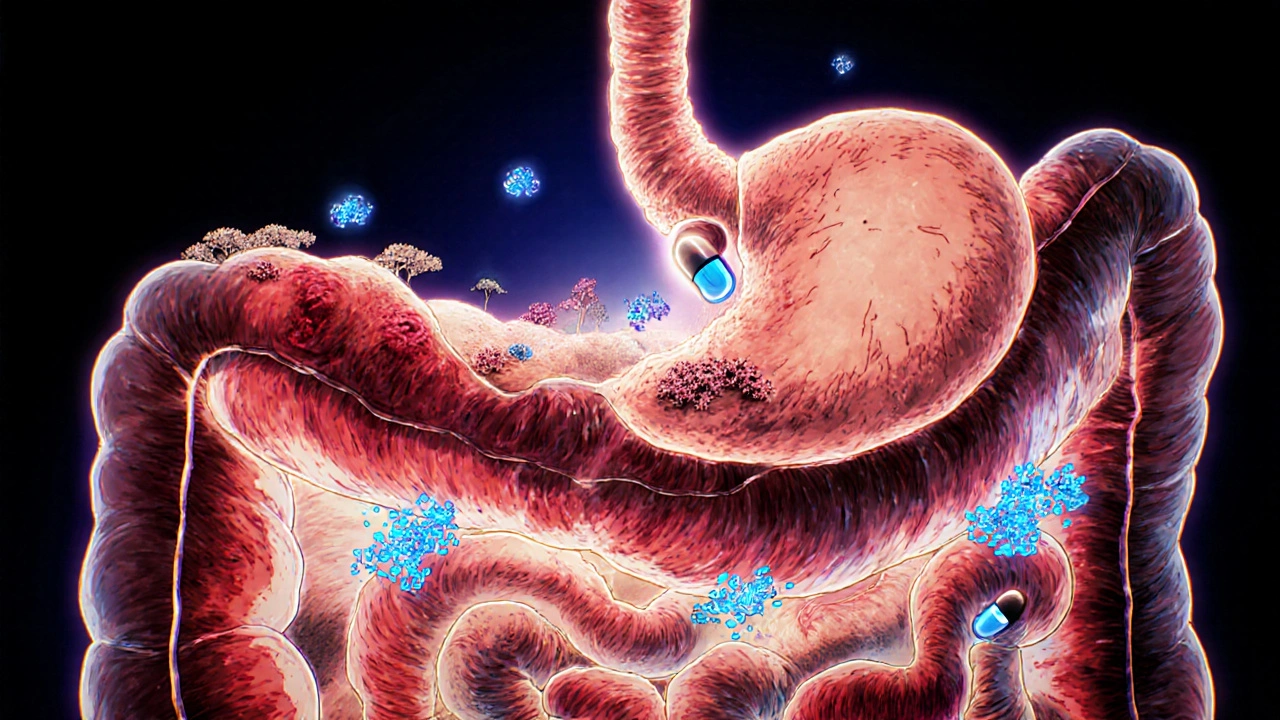
Gastrointestinal Medications: Why Absorption Problems Ruin Effectiveness
Nov 29, 2025, Posted by Mike Clayton
Many gastrointestinal medications fail to work because of poor absorption in the gut. Learn how food, disease, pH, and formulation affect drug effectiveness-and what you can do about it.
MORESEARCH HERE
Categories
TAGS
- treatment
- online pharmacy
- dietary supplement
- side effects
- generic drugs
- medication adherence
- medication safety
- health
- dietary supplements
- health benefits
- online pharmacy Australia
- generic substitution
- adverse drug reactions
- thyroid disorders
- gabapentin
- treatment option
- calcipotriol
- blood pressure
- erectile dysfunction
- closer look
